What's the Difference Between Plate & Roller Compaction Machinery?
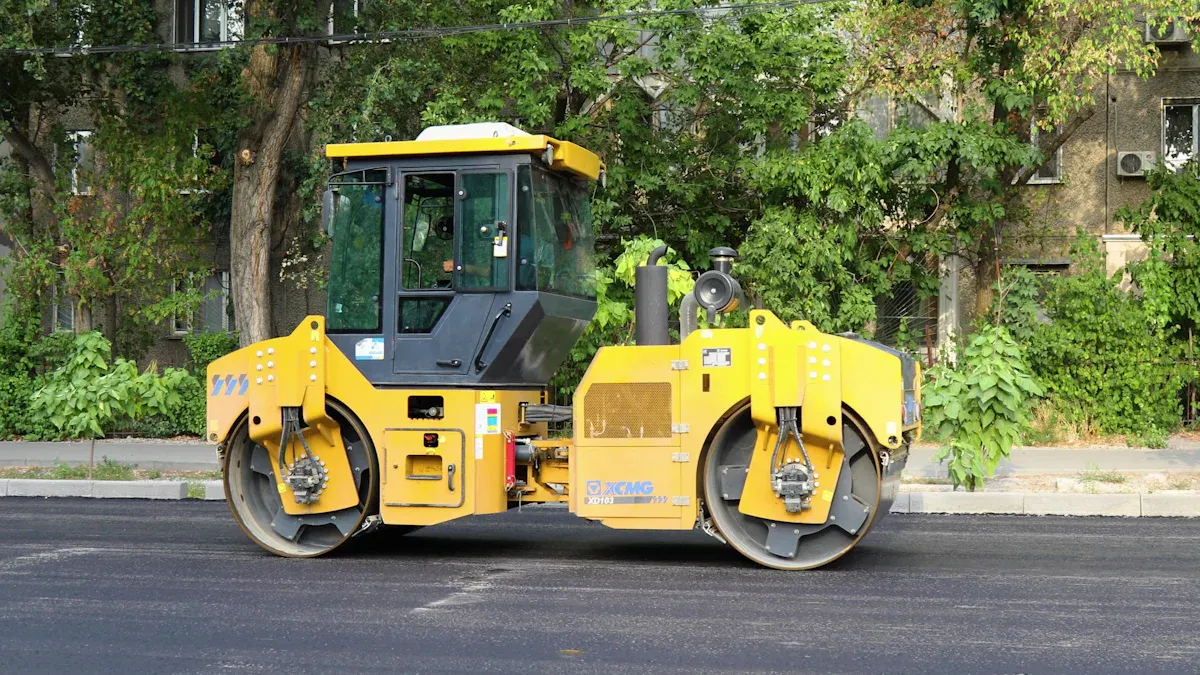

Plate compactors are ideal for granular soils and confined spaces. Roller Compactors suit larger areas and both granular and cohesive soils. These machines offer deeper compaction. MAXMACH provides a range of compaction solutions for various construction needs. Selecting the correct machinery ensures efficient and effective soil preparation.
Key Takeaways
- Plate compactors work best for small areas and granular soils like sand. They use vibration to compact the surface.
- Roller compactors are good for large areas and different soil types, including clay. They use heavy drums to compact deeply.
- Choose the right machine based on your project size and soil type. This helps ensure a strong and stable construction base.
Understanding Plate Compaction Machinery
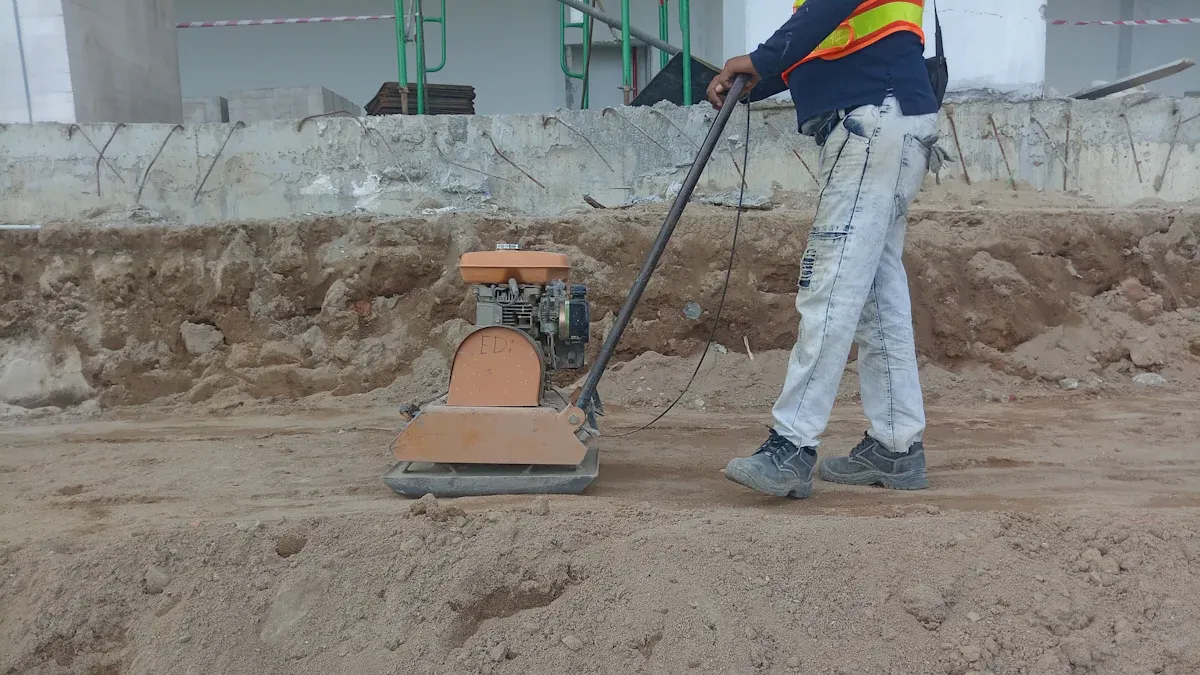

Plate compactors are vital tools in construction and landscaping. They prepare surfaces by increasing soil density. These machines are known for their effectiveness in smaller areas and for specific material types. They ensure a stable foundation for various projects.
How Plate Compactors Operate
A plate compactor features a heavy, flat base plate. An engine drives an eccentric weight, causing this plate to vibrate rapidly. This vibration generates a powerful, repetitive downward force. This force rearranges soil particles, making them settle closer together. It effectively removes air pockets from the material. This action significantly increases the soil's density and stability. Operators guide these machines across the surface, ensuring even compaction.
Types of Plate Compactors
The market offers several types of plate compactors. Forward plate compactors move only in one direction. They are suitable for general surface compaction on open sites. Reversible Plate Compactors provide greater maneuverability. They can move both forward and backward, which is ideal for working in confined spaces, such as trenches or around obstacles. Heavy-duty plate compactors are larger and heavier. They deliver superior compaction force for more demanding projects and thicker layers. MAXMACH provides a selection of these robust and efficient machines.
Common Applications for Plate Compactors
Plate compactors excel in specific applications. They efficiently compact granular materials like sand, gravel, and crushed stone. Contractors frequently use them for preparing stable bases for patios, walkways, and driveways. They are also indispensable for compacting backfill in narrow trenches for utility lines. Small asphalt repair jobs often benefit from the precise compaction a plate compactor offers. Landscaping projects widely employ these machines for ground preparation before laying sod or planting.
Understanding Roller Compaction Machinery
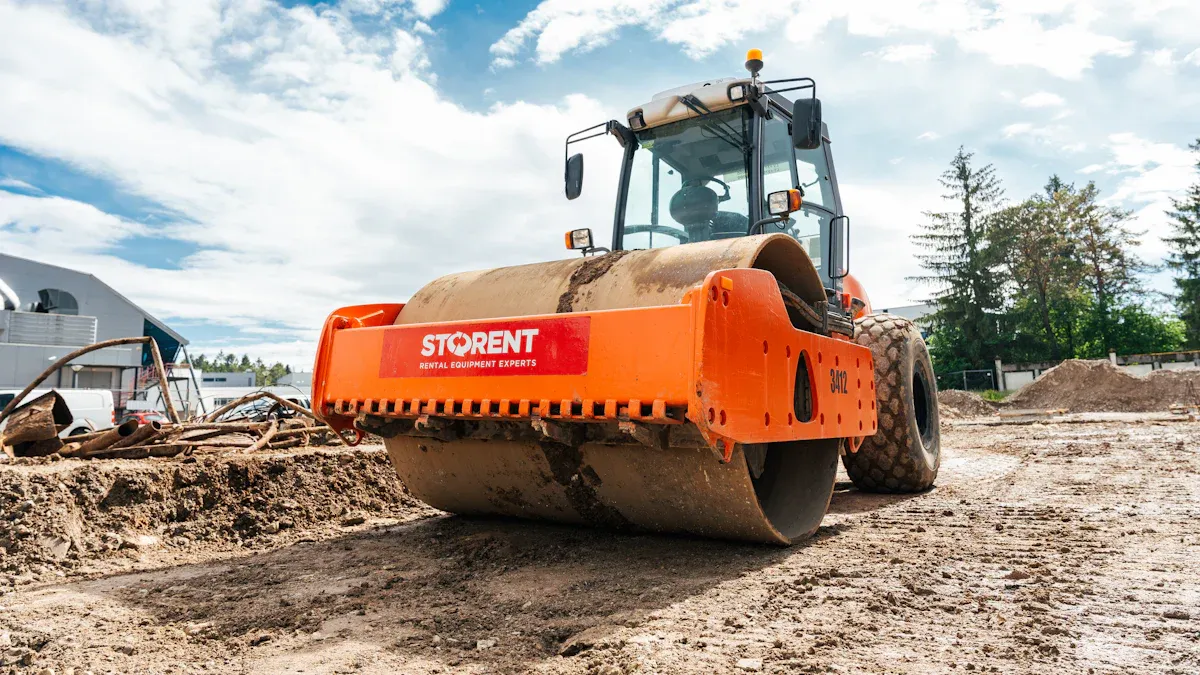

Roller compactors are powerful machines. They are crucial for large construction projects. These machines efficiently compact various soil types. They create stable foundations for extensive structures.
How Roller Compactors Operate
Roller compactors utilize heavy drums or wheels. These components apply significant static pressure. Many rollers also incorporate vibration. The machine's weight presses down on the material. The vibration then helps soil particles rearrange. This action removes air voids. It increases the material's density. Operators guide the roller across the surface. This process ensures uniform compaction. It creates a strong, stable base.
Types of Roller Compactors
The industry uses several types of roller compactors. Smooth drum rollers feature a flat steel drum. They compact granular materials and asphalt effectively. Padfoot or sheepsfoot rollers have lugs or "feet" on their drums. These rollers penetrate and compact cohesive soils like clay. Pneumatic tire rollers use multiple rubber tires. They achieve a kneading action. This action is ideal for asphalt and mixed soils. MAXMACH provides a diverse range of roller compactor models.
Common Applications for Roller Compactors
Roller compactors are indispensable for large-scale projects. They compact sub-bases for roads and highways. Construction teams use them for airport runways. Building foundations also require roller compaction. Landfill construction benefits from their deep compaction capabilities. These machines prepare vast areas for commercial developments. They ensure durable and stable ground conditions.
Key Differences: Plate vs. Roller Compaction
Understanding the fundamental distinctions between plate and roller compaction machinery is crucial for selecting the right equipment. Each machine offers unique advantages for specific project requirements.
Compaction Mechanism and Force
Plate compactors primarily use a vibratory force. An eccentric weight within the machine creates rapid, high-frequency vibrations. This action causes the base plate to strike the ground repeatedly. The impact force rearranges soil particles, removing air voids and increasing density. Plate compactors deliver force vertically, compacting from the surface downwards.
Roller compactors, conversely, employ a combination of static weight and dynamic force. Their heavy drums apply significant static pressure to the material. Many rollers also incorporate vibration, which adds a dynamic component. This vibration helps soil particles settle more efficiently. Rollers achieve compaction through a rolling action, distributing pressure over a larger area.
Soil Type Suitability
Plate compactors excel at compacting granular soils. These include sand, gravel, and crushed stone. Their vibratory action effectively interlocks these non-cohesive particles. Plate compactors are less effective on cohesive soils like clay, as the vibratory action struggles to break down the strong bonds between clay particles.
Roller compactors demonstrate versatility across various soil types. Smooth drum rollers work well on granular materials and asphalt. Padfoot or sheepsfoot rollers are specifically designed for cohesive soils. Their protruding feet knead and compact clay and silty soils. Pneumatic tire rollers handle mixed soils and asphalt, providing a kneading and sealing effect.
Area Coverage and Efficiency
Plate compactors are ideal for smaller areas and confined spaces. Their compact size allows operators to maneuver them easily around obstacles, in trenches, or along edges. They cover ground at a slower pace compared to rollers. This makes them suitable for localized compaction tasks.
Roller compactors cover large areas quickly and efficiently. Their wide drums or multiple tires allow them to compact significant stretches of land with each pass. This makes them indispensable for large-scale projects like road construction or airport runways. Their efficiency significantly reduces project timelines for extensive compaction needs.
Compaction Depth and Pressure
Plate compactors typically achieve shallower compaction depths. Their force concentrates near the surface. They are effective for compacting layers up to 6-12 inches, depending on the machine's weight and power. They apply high pressure over a small contact area.
Roller compactors achieve much deeper compaction. Their heavy weight and vibratory action penetrate several feet into the soil. This makes them essential for sub-base preparation and foundational work. They distribute pressure over a larger contact area, creating a more uniform and deeper compaction profile. MAXMACH offers rollers designed for maximum depth.
Maneuverability and Size
Plate compactors are relatively small and highly maneuverable. Operators can easily guide them by hand. Their compact design allows for transport in the back of a pickup truck or on a small trailer. This makes them convenient for jobs with limited access.
Roller compactors are large, heavy machines. They require specialized transport. Their size limits their maneuverability, especially in tight spaces. Operators typically use them in open areas where they can make wide turns and long passes. Their scale reflects their capacity for large-volume compaction.
When to Choose a Plate Compactor
Choosing the right compaction equipment is essential for project success. Plate compactors offer specific advantages for certain tasks. Project managers select them for their efficiency in particular conditions.
Small Projects and Tight Spaces
Plate compactors are ideal for small-scale construction and landscaping jobs. Their compact size allows easy maneuverability. Operators guide them effectively in confined areas. These include trenches for utility lines or narrow pathways. They also work well around obstacles like pipes or foundations. Transporting plate compactors is simple. They fit easily into a truck bed or small trailer. This makes them convenient for residential projects or sites with limited access.
Granular Soil Compaction
Plate compactors excel at compacting granular materials. These materials include sand, gravel, and crushed stone. Their vibratory action effectively interlocks these particles. This process removes air voids and increases density. They are not suitable for cohesive soils like clay. The machine's vibration struggles to break down the strong bonds in clay. For optimal results, use plate compactors on well-draining, non-cohesive soils.
Surface Compaction Needs
Plate compactors are best for achieving compaction near the surface. They create a stable, dense top layer. This is crucial for preparing bases for patios, walkways, and driveways. They also compact the top layers of backfill in trenches. While they do not achieve deep compaction, they provide excellent surface stability. MAXMACH offers plate compactors designed for reliable surface preparation. They ensure a firm foundation for various finishing materials.
When to Choose a Roller Compactor
Choosing the correct compaction equipment is vital for project success. Roller compactors offer distinct advantages for specific types of work. Project managers select them for their efficiency and power in particular conditions.
Large-Scale Project Requirements
Roller compactors are indispensable for extensive construction projects. They efficiently handle tasks like building roads, highways, and airport runways. These machines cover vast areas quickly. Their large size and powerful compaction capabilities make them ideal for projects requiring high efficiency. Project managers choose roller compactors when they need to process significant volumes of material. They ensure timely completion of large-scale infrastructure. Their broad coverage minimizes the number of passes required. This saves both time and labor on site.
Cohesive and Mixed Soil Compaction
Roller compactors demonstrate superior performance on cohesive and mixed soils. Padfoot rollers, with their unique drum design, effectively penetrate and compact clay and silty soils. Their "feet" break up clods and achieve uniform density. Pneumatic tire rollers use a kneading action. This action is perfect for compacting asphalt and various mixed soil types. Plate compactors struggle with these soil compositions. Roller compactors provide the necessary force to achieve proper density in challenging materials. They create a stable base where other machines might fail.
Deep Compaction Applications
Roller compactors excel in applications demanding deep soil compaction. Their heavy weight and powerful vibratory systems allow them to compact soil layers several feet deep. This capability is crucial for preparing stable sub-bases for major structures. They ensure the long-term stability of foundations and large earthworks. When projects require deep soil stabilization, roller compactors are the preferred choice. They effectively consolidate underlying layers, preventing future settlement. MAXMACH offers robust roller compactors for these demanding tasks, ensuring optimal ground preparation.
MAXMACH: When to Use Both Compaction Types
Sometimes, construction projects benefit most from using both plate and roller compaction machinery. This combined approach ensures comprehensive soil preparation. It addresses various site conditions and compaction requirements effectively.
Layered Compaction Strategies
Project managers often employ layered compaction strategies. They use roller compactors for deeper lifts of material. Rollers efficiently compact thick layers of soil or aggregate. After the initial deep compaction, plate compactors can refine the upper layers. This method ensures uniform density throughout the entire soil profile. It prevents weak spots and improves overall stability. This strategy is particularly useful for foundations and road bases.
Combining Surface and Deep Compaction
Combining both types of machinery allows for optimal compaction at different depths. Roller compactors handle the bulk of deep compaction. They create a solid, stable sub-base. Plate compactors then address surface-level needs. They compact granular materials for the final few inches. This ensures a smooth, dense surface ready for finishing. For example, a roller compacts the main roadbed. A plate compactor then compacts the edges or utility trenches.
Achieving Optimal Density Targets
Using both plate and roller compactors helps achieve precise density targets. Rollers provide the necessary force for deep, high-volume compaction. Plate compactors offer precision for specific areas or thinner layers. This dual approach ensures every part of the project meets required specifications. It leads to superior structural integrity and longevity. MAXMACH offers a range of equipment to support these comprehensive compaction strategies.
Choosing the right compaction machinery ensures project success. Project managers consider project size, soil type, and site accessibility for optimal results. This careful selection prevents costly errors. Proper operation and safety remain paramount for all compaction tasks. These practices protect workers and equipment.
FAQ
❓ What is the main purpose of soil compaction?
Soil compaction increases density. It removes air voids. This creates a stable base for construction. It prevents future settlement.
🚧 Can a plate compactor be used on all soil types?
No, plate compactors work best on granular soils. They struggle with cohesive soils like clay. Rollers are better for clay.
⏱️ How does a roller compactor save time on large projects?
Roller compactors cover large areas quickly. Their wide drums compact significant ground with each pass. This reduces project timelines efficiently.
 Internal Vibrator
Internal Vibrator  External Vibrator
External Vibrator  Submersible Pump
Submersible Pump  Eccentric shaft
Eccentric shaft  Pendulum shaft
Pendulum shaft  Portable vbrator shaft
Portable vbrator shaft  Portable concrete mixer
Portable concrete mixer  Vertical concrete mixer
Vertical concrete mixer  Hydraulic concrete mixer
Hydraulic concrete mixer  Walk behind power trowel
Walk behind power trowel  Ride on power trowel
Ride on power trowel  Concrete screed
Concrete screed  Tamping rammer
Tamping rammer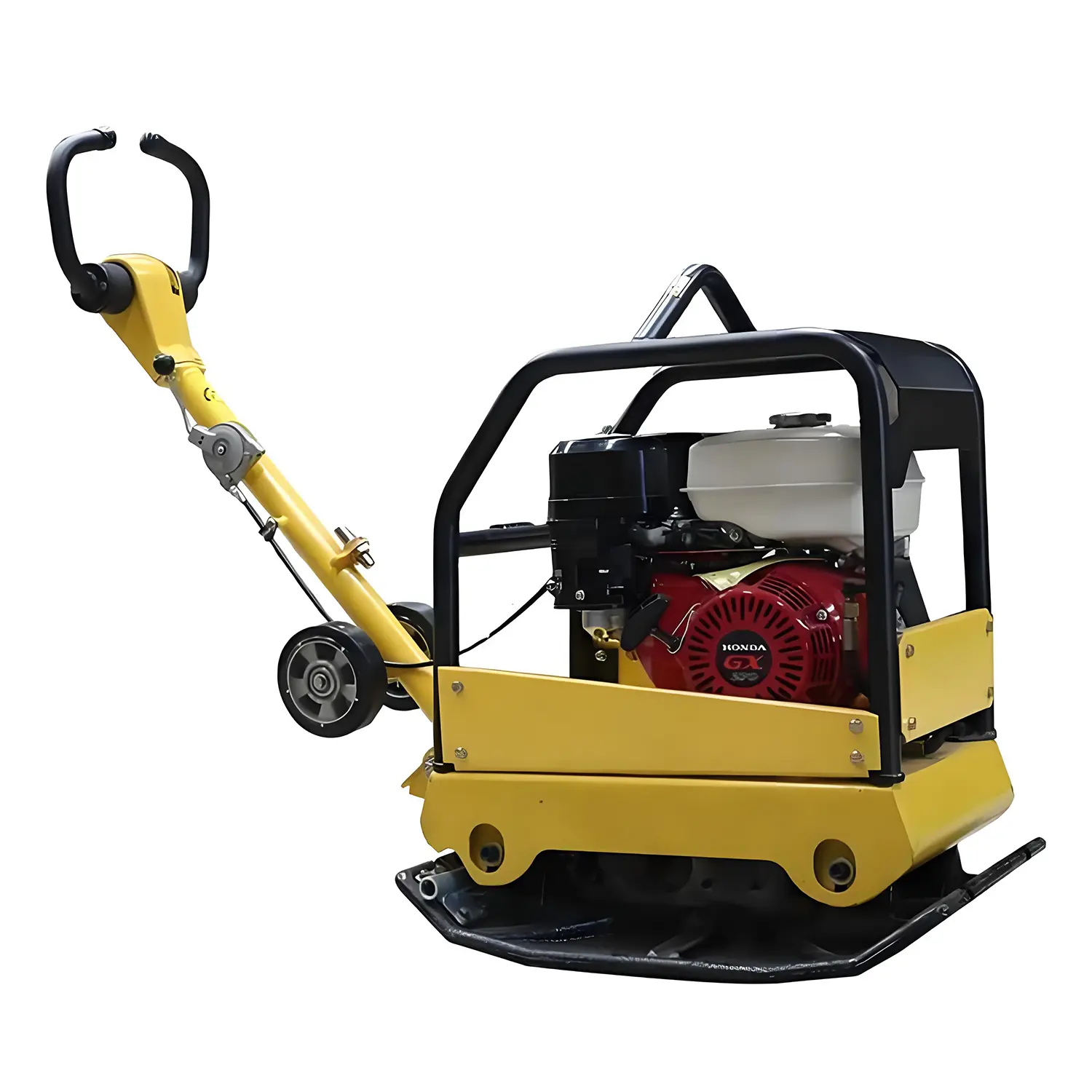  Plate compactor
Plate compactor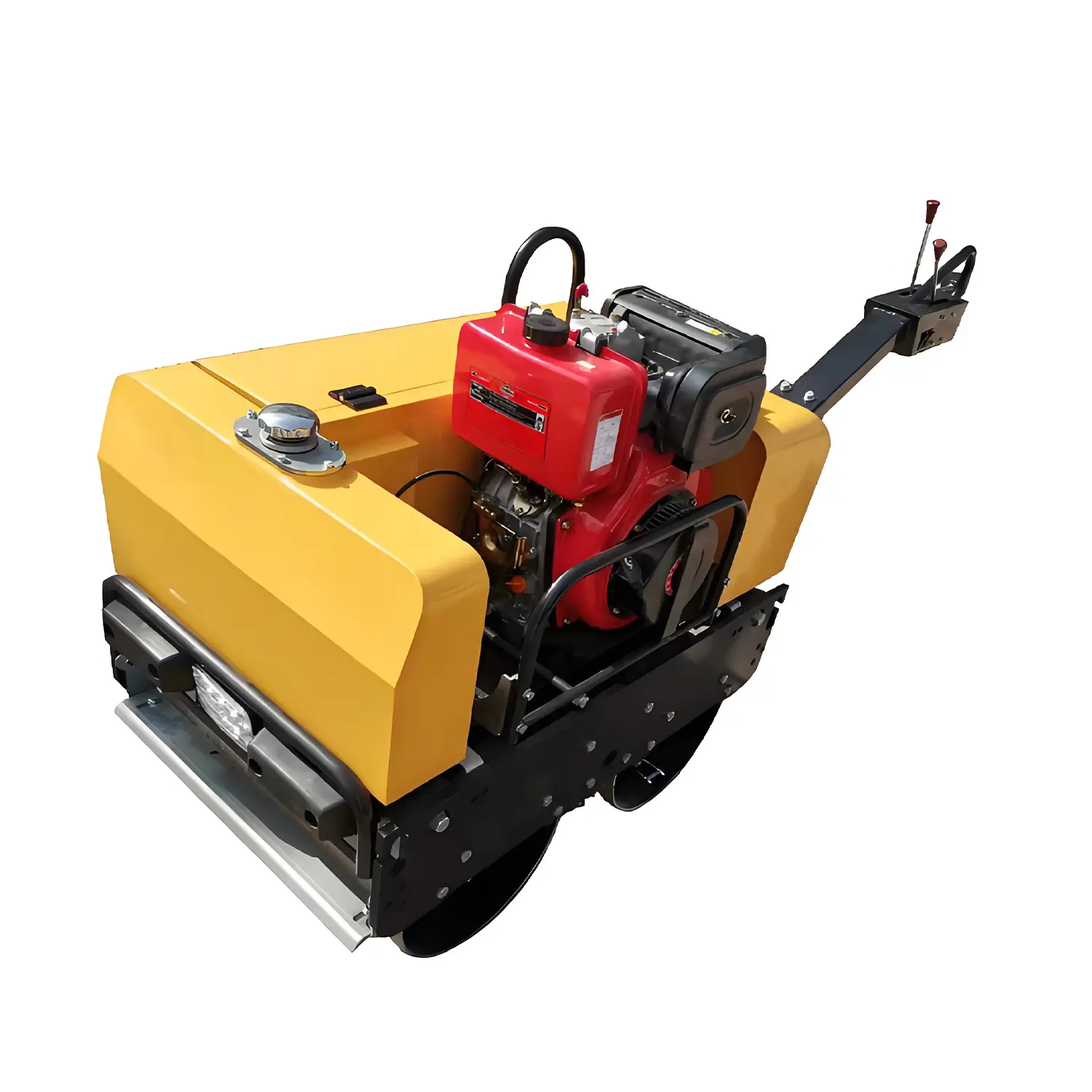  Vibratory roller
Vibratory roller